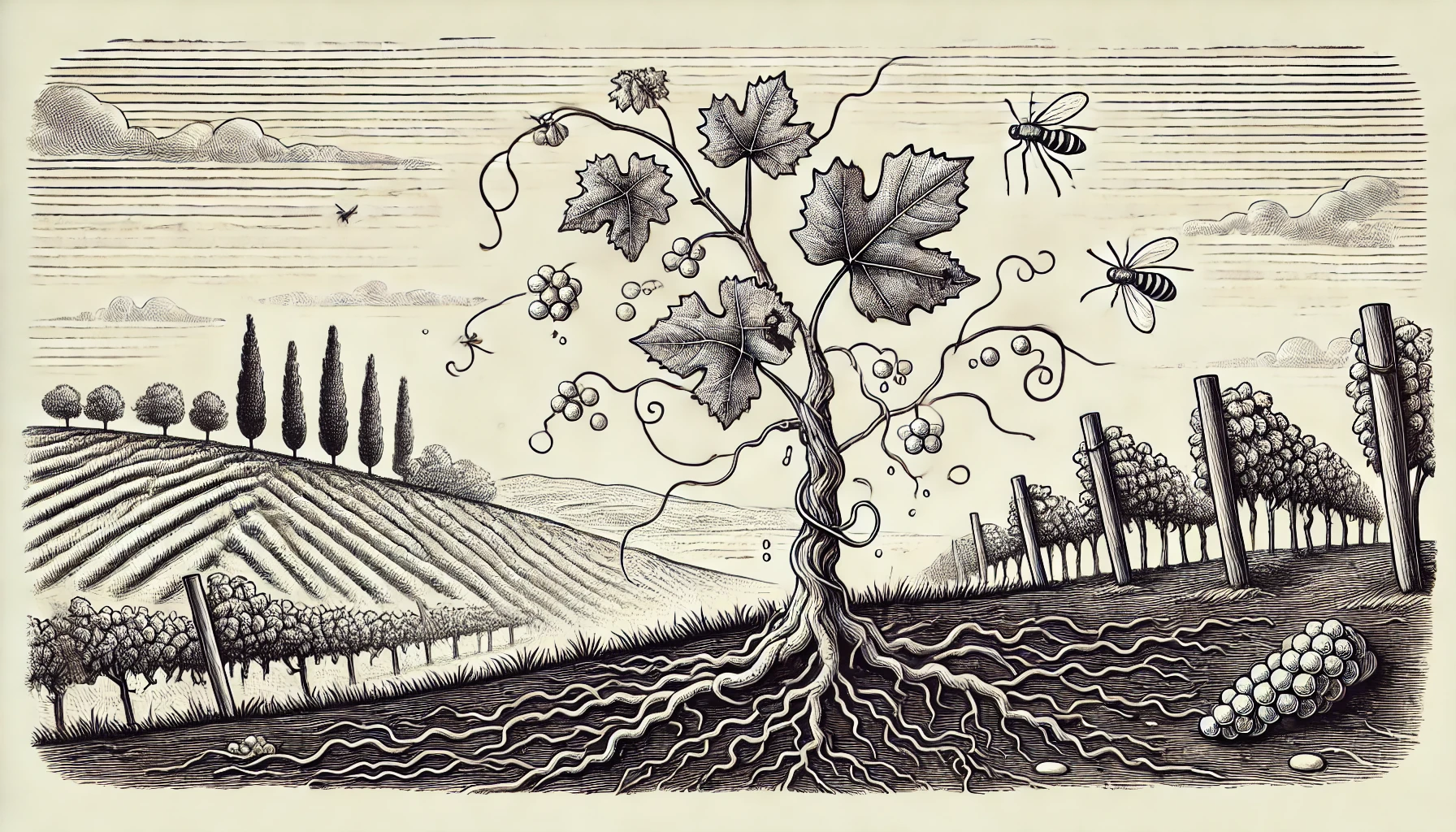
Phylloxera is a tiny, root-feeding insect that is infamous for causing one of the greatest catastrophes in the history of viticulture. In the 19th century, this pest devastated vineyards across Europe, particularly in France, by feeding on the roots of grapevines and spreading a deadly disease that caused the vines to wither and die.
Phylloxera was accidentally introduced to Europe from North America in the mid-1800s. North American grapevines had developed a natural resistance to Phylloxera, but European grapevines had no such defenses. As a result, the pest spread rapidly, wiping out vast swathes of vineyards and threatening the very survival of the wine industry.
The solution to the Phylloxera crisis came in the form of grafting—attaching European grapevines (Vitis vinifera) to the roots of American grapevines (Vitis labrusca), which were resistant to the pest. This practice of grafting European vines onto American rootstock became widespread, allowing the wine industry to recover. Today, most vineyards around the world still use this grafting technique to protect their vines from Phylloxera.
Despite this solution, Phylloxera remains a concern in some parts of the world, particularly in regions where ungrafted vines are grown. The history of Phylloxera serves as a reminder of the vulnerability of grapevines and the importance of viticultural practices that help protect vineyards from pests and disease.
Curious about more wine terms and insights? Visit our Wine Wiki section and explore the basic wine terms for expert definitions and tips!